
Learn residential, commercial and industrial electrical installation accordant with the National Electrical Code (NEC) in an 8 month, hands-on program aimed at preparing you for a range of electrical professions.
8 Months
AM/PM Classes
On-Campus or Online
California DIR approved provider of the whole general electrician curriculum.
general electrician curriculum.
Request More Info
Submit form for more program information.
We Respect Your Privacy. Information submitted on this form is sent to the SCIT Admissions Department and is not shared with any third parties.
Request More Info
Submit form for more program information.
We Respect Your Privacy
Information submitted on this form is sent to the SCIT Admissions Department and is not shared with any third parties.
Key Program
TOPICS
The following are some key topics studied in the General Electrician program:
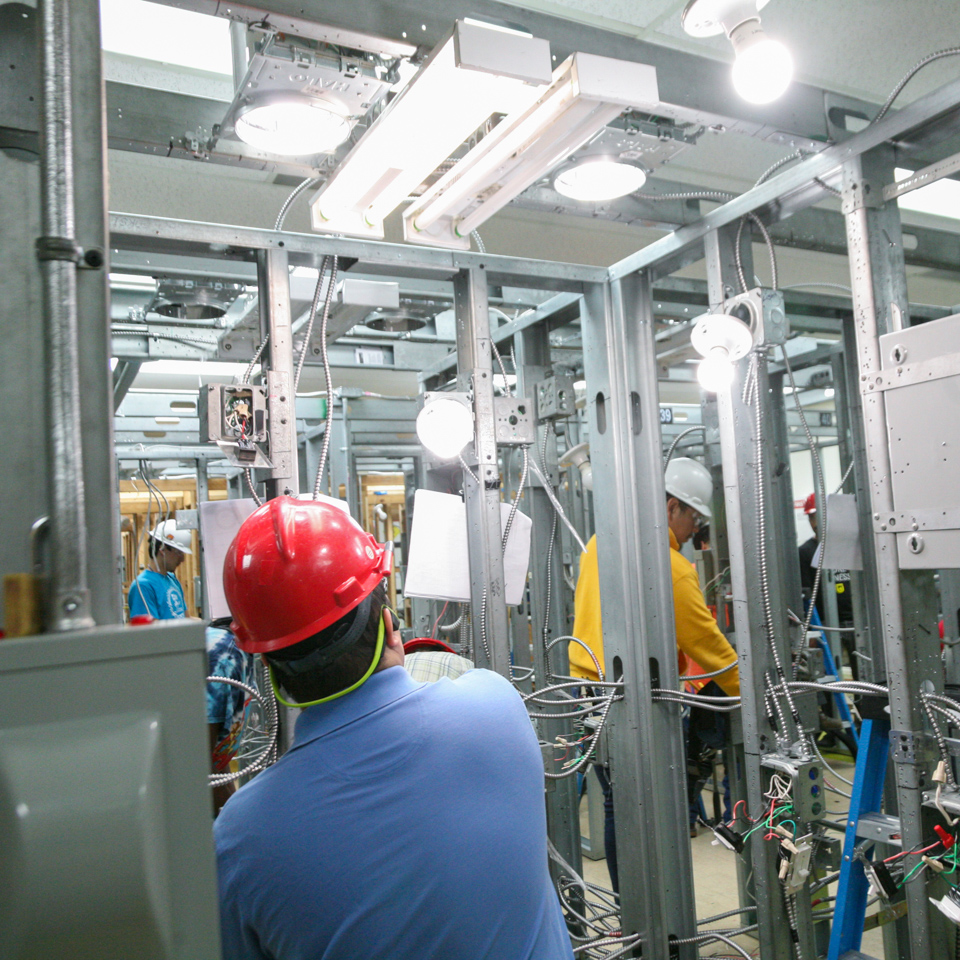
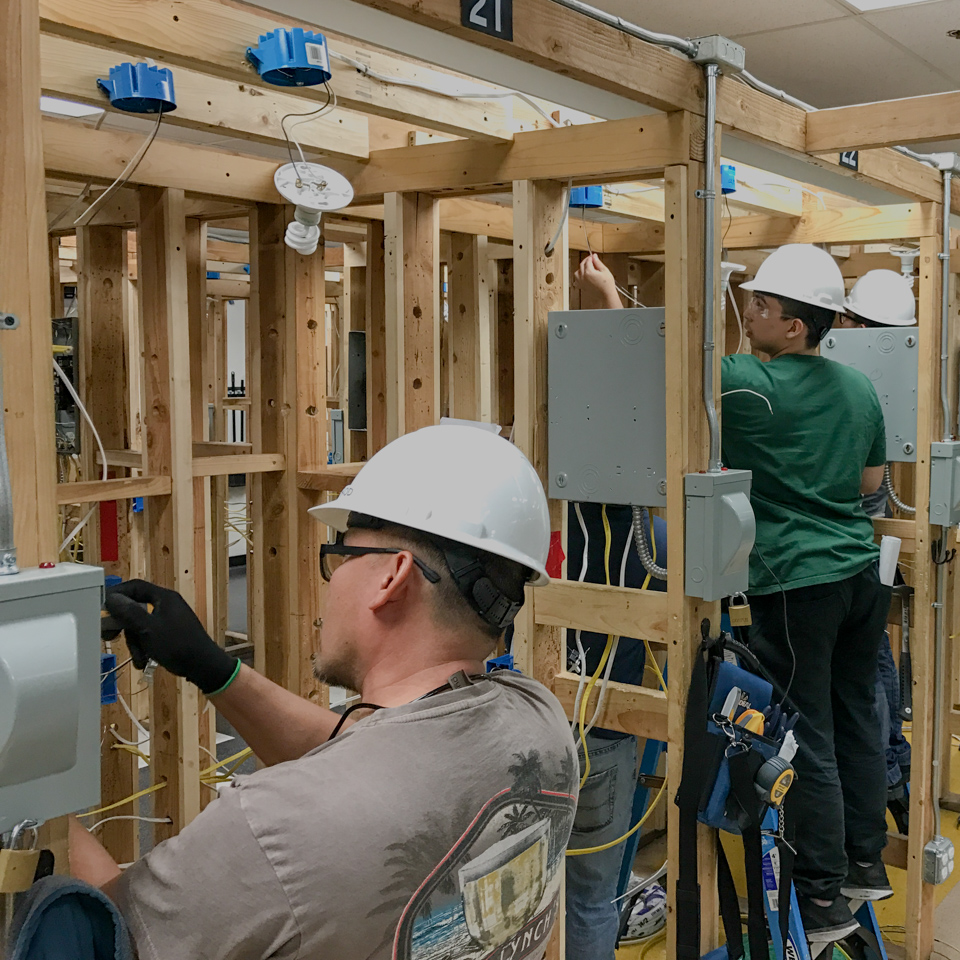
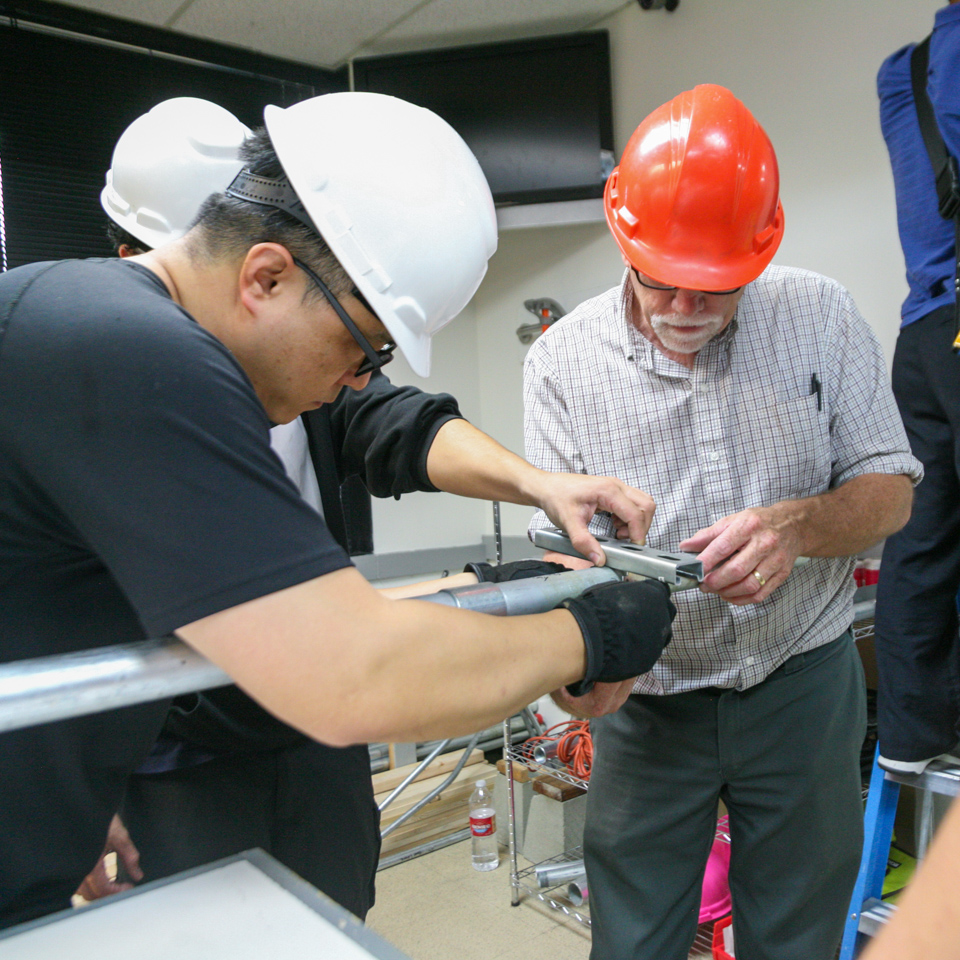
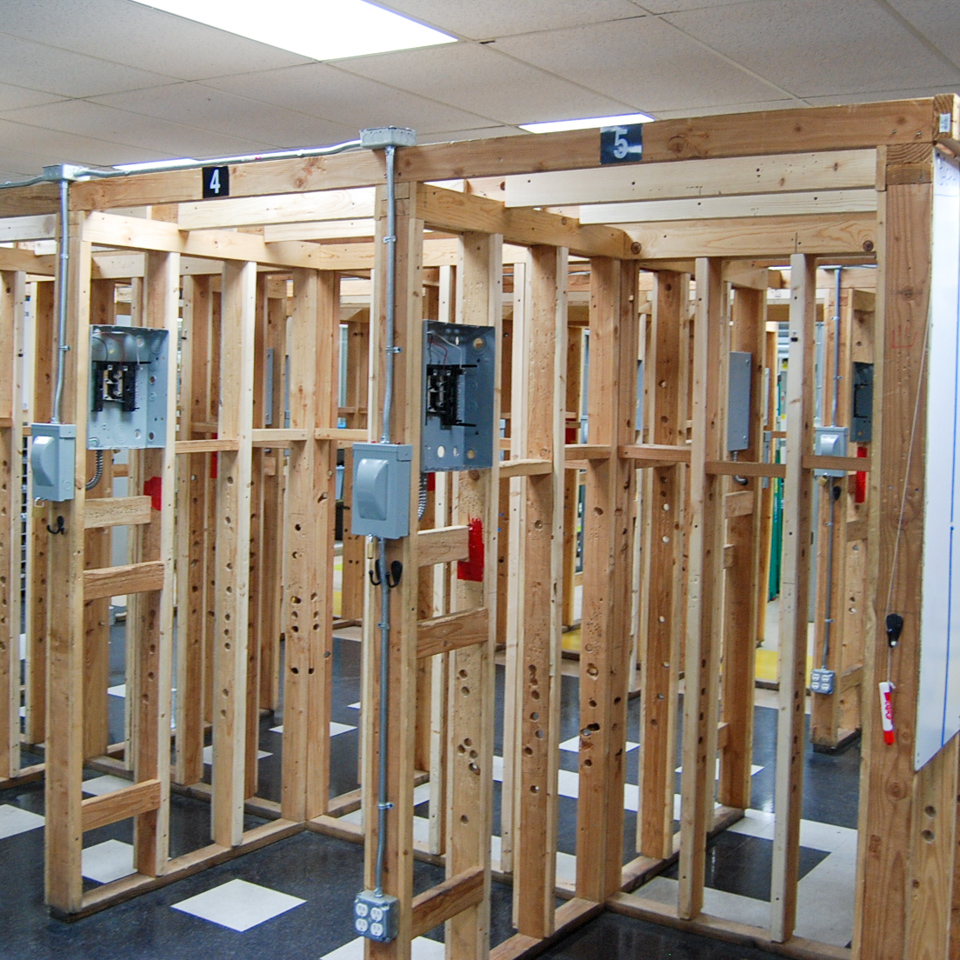
Learn how to apply the NEC code as it relates to electrical installation of residential and commercial job sites by wiring switches, receptacles, light fixtures, electrical panels, and much more.
Study a wide range of the NEC, branching into a variety of specialty topics to include installation of renewable energy sources (i.e. solar panels and wind turbines), low voltage wiring, alarm system installation, and more.
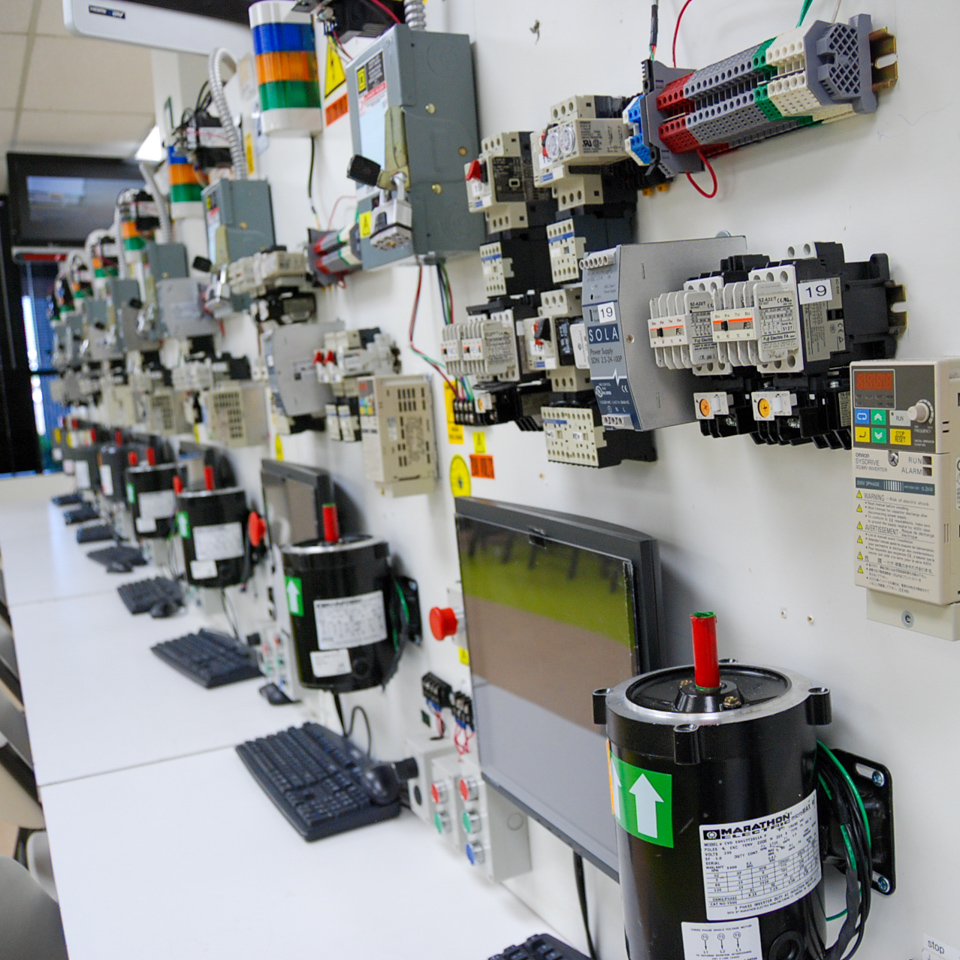
Train to install, control and troubleshoot electric motors used in a variaty of commercial and industrial applications.
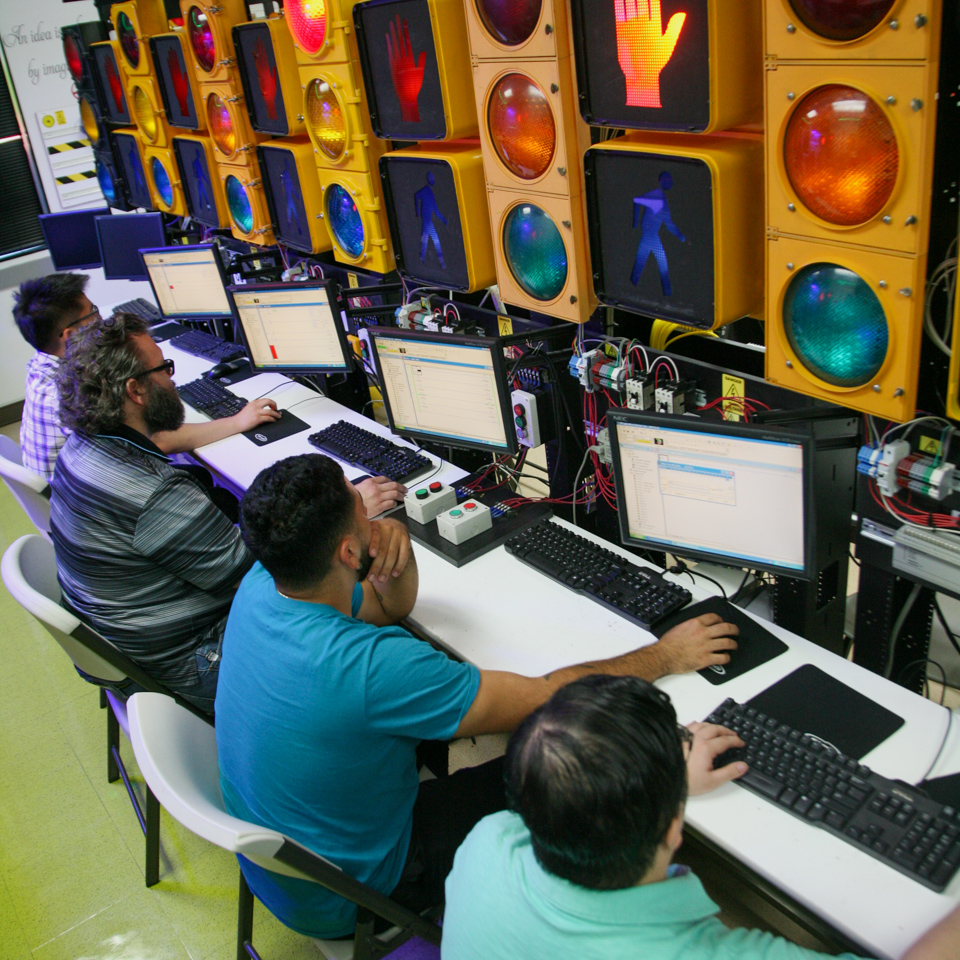
Learn to perform ladder logic programming of Allen Bradley programmable logic controllers (PLC) to perform a variety of industrial simulations involving a broad range of electrical and electromechanical inputs and outputs.



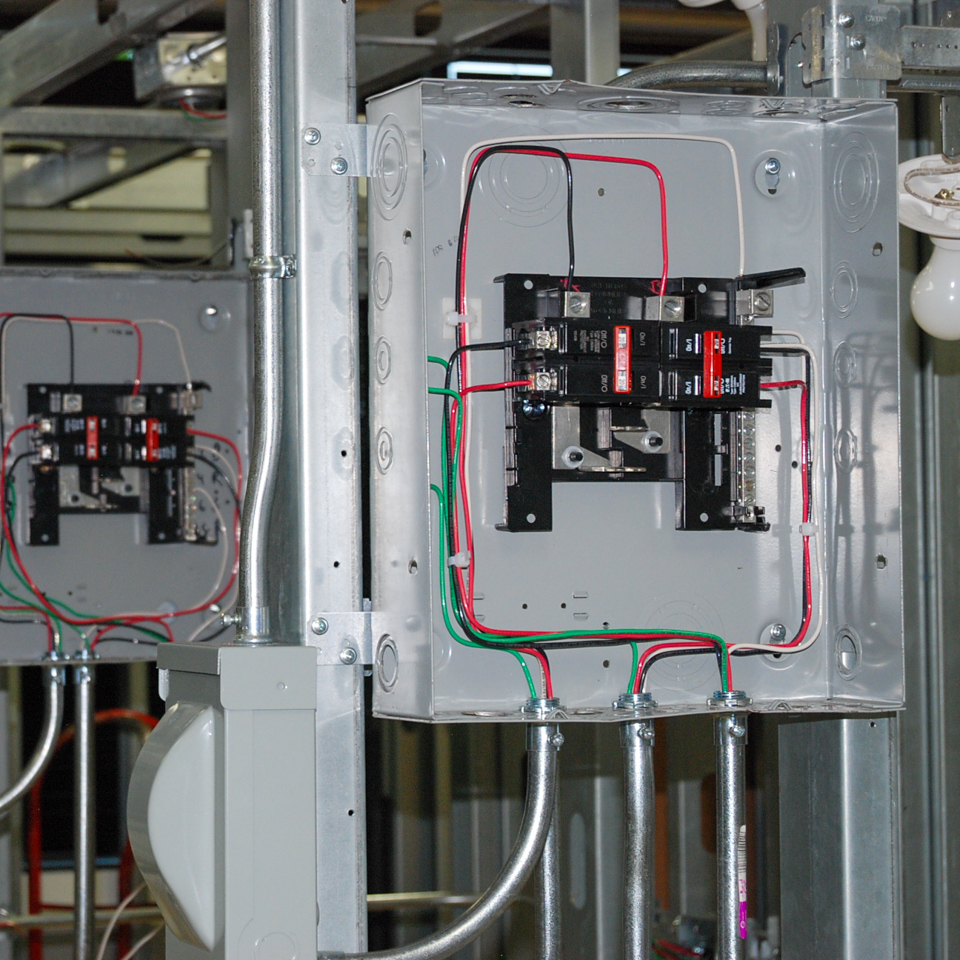


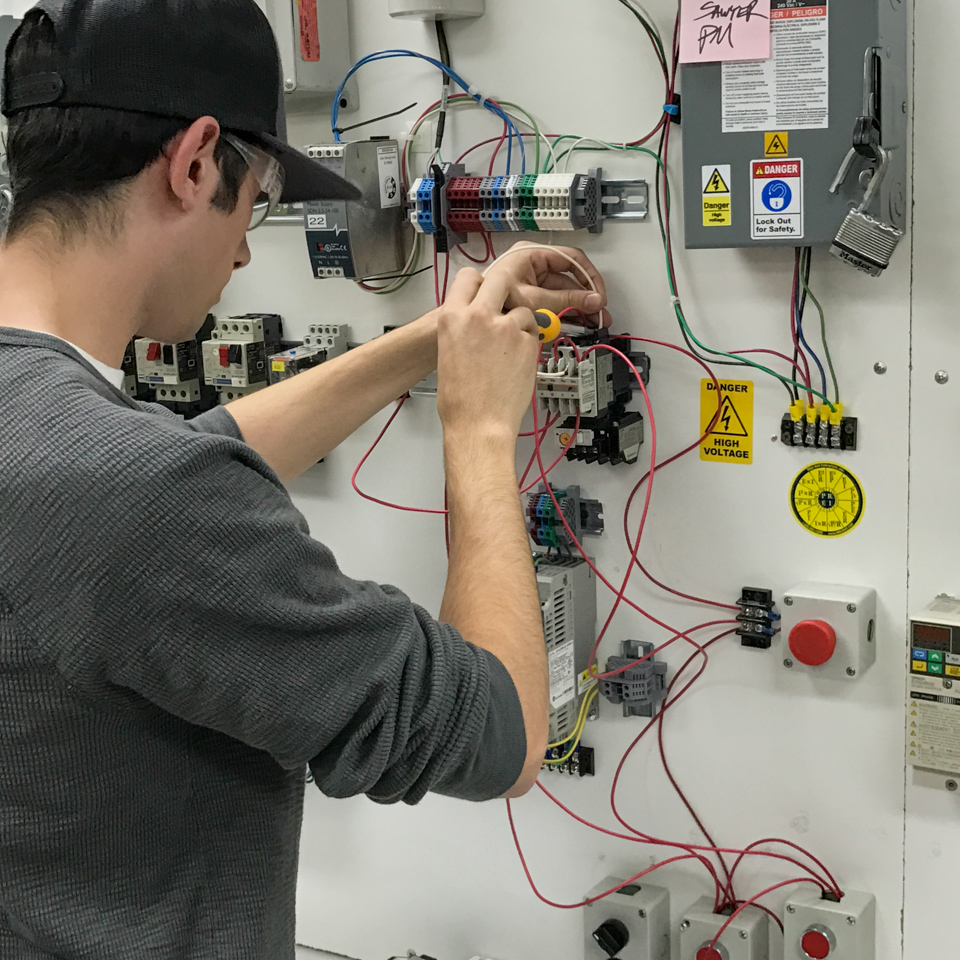






B.S. Electrical Engineering Degree Opportunities
Students may have the opportunity to continue their education toward a degree to open further career opportunities.
Electrical Career Pathway
Start by completing the General Electrician program and find entry level employment in the electrical field. Work in the field while pursuing a B.S. Electrical Engineering degree in the evenings. At the end you will have a diploma, a degree and work experience.
An Electrical Engineering bachelor’s degree may also reduce the amount of work experience that the State of California requires for those wanting to take the C-10 Electrical Contractor Licensing Test.
Learn more about BSEE program.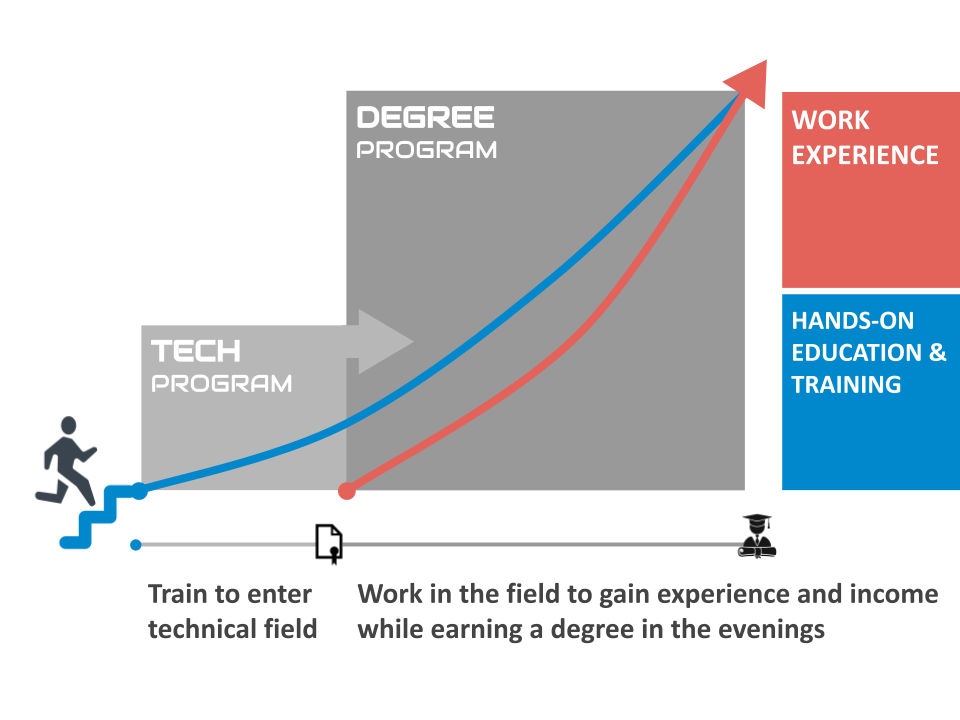
Degree Topics Include: Digital Electronics, Semiconductors and Circuits, Programming, MATLAB, Signal Analysis, Computer Aided Drafting (CAD), 3D Modeling with SolidWorks, Embedded Systems, Robotic Engineering, Control Systems, Electric Machines, Power Systems, Power Distribution, Power Protection, Senior Capstone Project and much more.
Support to Reach Your Goals
The Student Services and Career Services Offices support you on your educational path to greater career opportunities.
Academic Support: Advisement, academic monitoring, tutoring, and more...
Career Support: Resume assistance, career workshops, job leads, and more...
Visit
The SCIT Campus!
Meet our staff and faculty,
tour our classrooms and labs, and
learn about our programs.
Call, email or request info to schedule.
CALL ADMISSIONS
SEND AN EMAIL
BOOK AN APPOINTMENT



Visitation appointments are usually made on Mondays-Fridays, between 10am and 5pm (except holidays).






